Metal Soft Magnetic Material
Product name : Metal Soft Magnetic Material
Model No. : GMG1-SM
Products Category: > Soft Magnetic Materials

Soft Magnetic Material
Material can be divided into ferromagnetism, ferrimagnetism, paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and anti-ferromagnetism based on their magnetism behavior and bulk magnetic susceptibility. Materials with ferromagnetism or ferrimagnetism are collectively referred to as magnetic materials. Magnetic materials can be further subdivided into soft magnetic materials, permanent magnetic materials, gyromagnetic materials, rectangular hysteresis materials, and piezomagnetic materials. Soft magnetic materials which otherwise known as soft magnet, is a corresponding concept against hard magnet. Those unfamiliar with magnetism are easy to misinterpret “soft” and “hard” from literally or material hardness, then mistake soft magnet for rubber magnet. In reality, the words “hard” and “soft” here is not mechanical but magnetism. Soft magnetic material is a type of magnetic material which able to quickly respond to change of the external magnetic field and obtain high magnetic flux density under low loss. Soft magnet possesses low coercivity and high permeability, therefore, it can be easily magnetized and demagnetized. Soft magnetic material is widely used in magnetic cores of transformers, inductors, motors, and generators.
Metal Soft Magnetic Material
Metal soft magnetic material is one of the most widely used magnetic material. The frequently used metal soft magnetic material includes pure iron, silicon steel and permalloy. The application of metal soft magnetic material in the industry has a history of more than one hundred years and its development can be divided into four stages. The period before 1930s can be generally regarded as the first stage in the development of metal soft magnetic material. With the emergence of the electric power industry and telecommunication engineering, low-carbon steel began to produce transformer and motor at end of 19th century. Replacing steel by silicon steel effectively reduced loss at the beginning of the 20th century and silicon steel still ranks first for soft magnet demand in power industry up to now. Meanwhile, weak current engineering laid down high permeability requirement for material with the progress of telephony, then an array of soft magnetic alloys emerged as the time require. By the 1920s, the rise of radio technology further promoted the development of high permeability soft magnetic alloy, then permalloy, mu-metal, perminval alloy, hiperco alloy and permalloy powder core appeared. Metal soft magnetic material experienced the second stage of development between 1930s and 1940s, then its variety, magnetic properties and application have been developed rapidly during this period. The representative achievements includes multi-element permalloy, FeSiAl high permeability alloy and unidirectional silicon steel. Meanwhile, researchers found that magnetic heat treatment and rolling can establish induced anisotropy in the permalloy and studied ordered lattice tructure in the permalloy and iron-cobalt alloy. In addition, magnetic physics have also made considerable headway such as proposed spin-wave theory and the energy band theory of ferromagnetism; magnetic domain and structural theory of domain wall; coercivity theory and technical magnetization theory; and mechanism of magnetic loss. Metal soft magnetic materials underwent the third process of development between 1940s and 1970s. Adventure and development of emerging technology put forward higher request to magnetoelectric properties of metal soft magnetic material, especially electronic technology and instruments. Representative materials in this period include high rectangular hysteresis loop alloy, high permeability alloy, magnetic thin film, soft magnetic aooly strip and doubly oriented silicon steel. Furthermore, researchers measured magnetocrystalline anisotropy constant and saturation magnetostriction constant of various soft magnetic alloys, studied the origin of high permeability and clarified the mechanism of magnetic heat treatment. Since 1970s, the development of metal soft magnetic materials entered into the fourth stage. Besides high efficiency, high stability and durability, metal soft magnet are required to possess a low cost. Researchers studied the relationship between magnetic performance and various factors in metallurgy, and change rule between material properties and various external conditions.
▲Production Classification Metal Soft Magnetic Material

⊙ Pure Iron

Pure iron is the earliest and commonly used pure metal soft magneitc material. Pure iron is referring to the low-carbon steel with a purity of over 99.85% iron and a maximum carbon content of 0.04%. In addition to the excellent steel cleanliness, pure iron also has many distinctive characteristics including outstanding corrosion resistance, admirable hot/cold forming capability, low smelting cost and suitable for all types of welding. As an electromagnetic material, pure iron possesses relatively high saturated magnetization Bs and maximum permeability μmax, low coercivity Hc, steady magnetic properties and good DC soft magnetic properties. Therefore, pure iron is mainly used to produce iron core and magnetic pole of an electromagnet; magnetic circuit of an electric relay and speaker; various parts for induction type and electromagnetic type measurement instruments; and magnetic pole to guide magnetic flux in the motor.
● Electromagnetic Properties of Pure Iron:
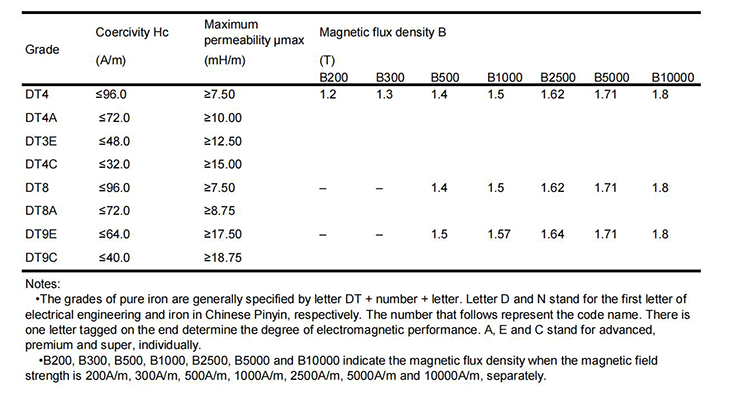
⊙ Silicon Steel
![]()
Pure iron will suffer from eddy current loss under alternating current (AC) magnetic field and thus can only operate direct current (DC) magnetic field. In order to overcome this drawback, a small amount of silicon is added to pure iron to form solid solution so that improve electrical resistivity of the alloy and reduce eddy current loss. Silicon steel, which also referred as electrical steel, is an iron alloy with silicon content between 1.5% and 4.5%. Silicon steel can be also divided to hot-rolled steel and cold-rolled steel on the basis of rolling technology. Besides, it also can be grouped in grain-oriented steel and non grain-oriented steel accordingly to the grain orientation. Electrical steel is usually manufactured in strips less than 2mm thick and then cut to specific shape to make laminations which are stacked together to form the laminated cores of transformers, and stator or rotor of electric motors.
⊙ Permalloy
Iron-nickel based soft magnetic alloys with 30-90% nickel content is collectively referred to as Permalloy. Permalloy is invented in 1914 by physicist Gustav Elmen at Bell Telephone Laboratories and then became a distinguished name of magnetism. Permalloy is notable for its very high magnetic permeability which make it useful as magnetic core material and magnetic shielding material under the weak magnetic field. Besides high permeability, its other magnetic properties are including low coercivity, near zero magnet ositriction, and significant anisotropic magnetoresistance. Grades of permalloy are typically specified by Arabic numbers 1+letter J+two numbers. Arabic numerals 1 stand for soft magnet. Letter J that follows represent the precision alloy. The two numbers tagged on the end determine the nickel content in the alloy. The commonly used grades include 1J50, 1J79 and 1J85. In addition to composition range, magnetic performance of Permalloy also can be adjusted by the heat treatment process.
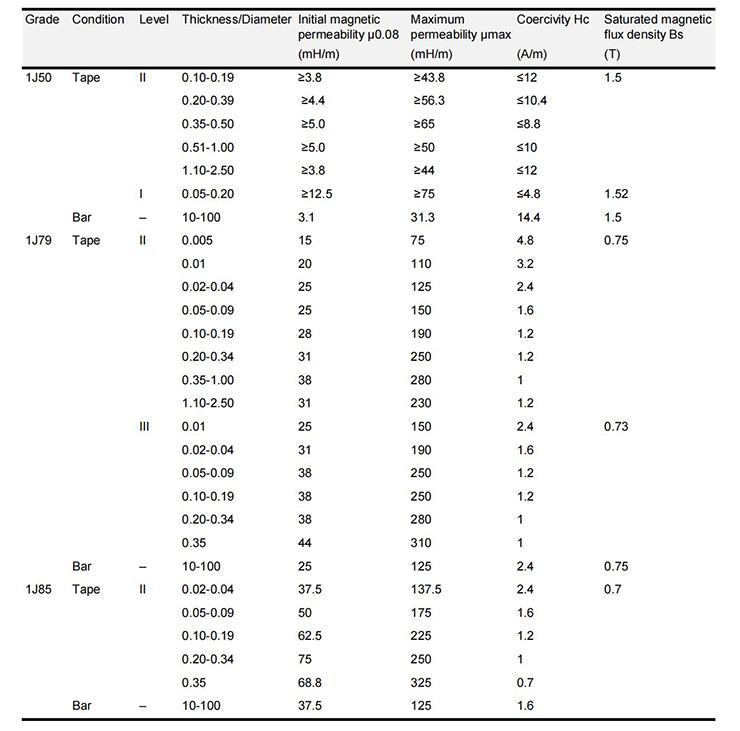
● Electromagnetic Properties of Permalloy
○ Electromagnetic Properties of High Permeability Permalloy
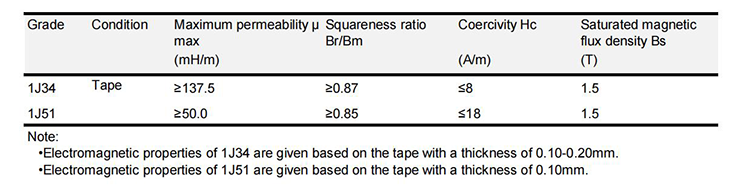
○ Electromagnetic Properties of High Rectangular Ratio Permalloy
○ Electromagnetic Properties of Magnetic Temperature Compensation Permalloy
-4_00-2157926.png)
---The End---
Send Inquiry :
Products Category
Featured Products
Contact Us
Name: April Yang
Tel: 0086-1560-1120-906
E-mail: [email protected]
Add: No. 18, Sihai Road, BDA, Beijing, China
Whatsapp: 0086 1560 1120 906
Wechat: 0086 1560 1120 906
QQ: 1013104078










